
Home » Tips for Teachers » 7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives

7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives
In recent years, the question of why students should not have homework has become a topic of intense debate among educators, parents, and students themselves. This discussion stems from a growing body of research that challenges the traditional view of homework as an essential component of academic success. The notion that homework is an integral part of learning is being reevaluated in light of new findings about its effectiveness and impact on students’ overall well-being.

The push against homework is not just about the hours spent on completing assignments; it’s about rethinking the role of education in fostering the well-rounded development of young individuals. Critics argue that homework, particularly in excessive amounts, can lead to negative outcomes such as stress, burnout, and a diminished love for learning. Moreover, it often disproportionately affects students from disadvantaged backgrounds, exacerbating educational inequities. The debate also highlights the importance of allowing children to have enough free time for play, exploration, and family interaction, which are crucial for their social and emotional development.
Checking 13yo’s math homework & I have just one question. I can catch mistakes & help her correct. But what do kids do when their parent isn’t an Algebra teacher? Answer: They get frustrated. Quit. Get a bad grade. Think they aren’t good at math. How is homework fair??? — Jay Wamsted (@JayWamsted) March 24, 2022
As we delve into this discussion, we explore various facets of why reducing or even eliminating homework could be beneficial. We consider the research, weigh the pros and cons, and examine alternative approaches to traditional homework that can enhance learning without overburdening students.
Once you’ve finished this article, you’ll know:
- Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts →
- 7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework →
- Opposing Views on Homework Practices →
- Exploring Alternatives to Homework →
Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts: Diverse Perspectives on Homework
In the ongoing conversation about the role and impact of homework in education, the perspectives of those directly involved in the teaching process are invaluable. Teachers and education industry experts bring a wealth of experience and insights from the front lines of learning. Their viewpoints, shaped by years of interaction with students and a deep understanding of educational methodologies, offer a critical lens through which we can evaluate the effectiveness and necessity of homework in our current educational paradigm.
Check out this video featuring Courtney White, a high school language arts teacher who gained widespread attention for her explanation of why she chooses not to assign homework.
Here are the insights and opinions from various experts in the educational field on this topic:
“I teach 1st grade. I had parents ask for homework. I explained that I don’t give homework. Home time is family time. Time to play, cook, explore and spend time together. I do send books home, but there is no requirement or checklist for reading them. Read them, enjoy them, and return them when your child is ready for more. I explained that as a parent myself, I know they are busy—and what a waste of energy it is to sit and force their kids to do work at home—when they could use that time to form relationships and build a loving home. Something kids need more than a few math problems a week.” — Colleen S. , 1st grade teacher
“The lasting educational value of homework at that age is not proven. A kid says the times tables [at school] because he studied the times tables last night. But over a long period of time, a kid who is drilled on the times tables at school, rather than as homework, will also memorize their times tables. We are worried about young children and their social emotional learning. And that has to do with physical activity, it has to do with playing with peers, it has to do with family time. All of those are very important and can be removed by too much homework.” — David Bloomfield , education professor at Brooklyn College and the City University of New York graduate center
“Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. In high school it’s larger. (…) Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. It’s one of those lower hanging fruit that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, ‘Is it really making a difference?’” — John Hattie , professor
”Many kids are working as many hours as their overscheduled parents and it is taking a toll – psychologically and in many other ways too. We see kids getting up hours before school starts just to get their homework done from the night before… While homework may give kids one more responsibility, it ignores the fact that kids do not need to grow up and become adults at ages 10 or 12. With schools cutting recess time or eliminating playgrounds, kids absorb every single stress there is, only on an even higher level. Their brains and bodies need time to be curious, have fun, be creative and just be a kid.” — Pat Wayman, teacher and CEO of HowtoLearn.com
7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework
Let’s delve into the reasons against assigning homework to students. Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices.
1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences

The ongoing debate about homework often focuses on its educational value, but a vital aspect that cannot be overlooked is the significant stress and health consequences it brings to students. In the context of American life, where approximately 70% of people report moderate or extreme stress due to various factors like mass shootings, healthcare affordability, discrimination, racism, sexual harassment, climate change, presidential elections, and the need to stay informed, the additional burden of homework further exacerbates this stress, particularly among students.
Key findings and statistics reveal a worrying trend:
- Overwhelming Student Stress: A staggering 72% of students report being often or always stressed over schoolwork, with a concerning 82% experiencing physical symptoms due to this stress.
- Serious Health Issues: Symptoms linked to homework stress include sleep deprivation, headaches, exhaustion, weight loss, and stomach problems.
- Sleep Deprivation: Despite the National Sleep Foundation recommending 8.5 to 9.25 hours of sleep for healthy adolescent development, students average just 6.80 hours of sleep on school nights. About 68% of students stated that schoolwork often or always prevented them from getting enough sleep, which is critical for their physical and mental health.
- Turning to Unhealthy Coping Mechanisms: Alarmingly, the pressure from excessive homework has led some students to turn to alcohol and drugs as a way to cope with stress.
This data paints a concerning picture. Students, already navigating a world filled with various stressors, find themselves further burdened by homework demands. The direct correlation between excessive homework and health issues indicates a need for reevaluation. The goal should be to ensure that homework if assigned, adds value to students’ learning experiences without compromising their health and well-being.
By addressing the issue of homework-related stress and health consequences, we can take a significant step toward creating a more nurturing and effective educational environment. This environment would not only prioritize academic achievement but also the overall well-being and happiness of students, preparing them for a balanced and healthy life both inside and outside the classroom.
2. Inequitable Impact and Socioeconomic Disparities
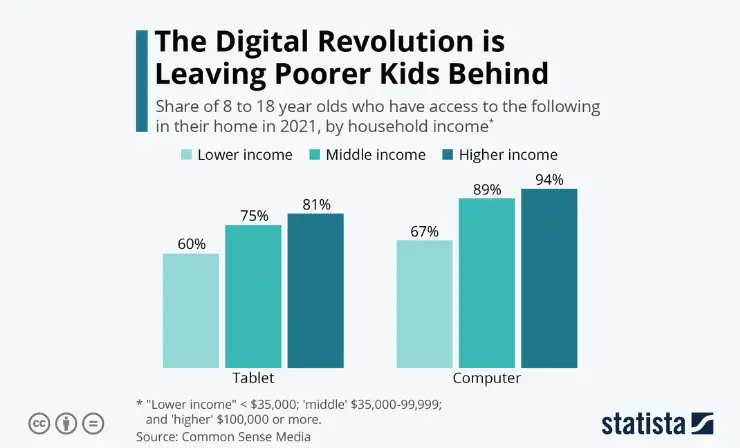
In the discourse surrounding educational equity, homework emerges as a factor exacerbating socioeconomic disparities, particularly affecting students from lower-income families and those with less supportive home environments. While homework is often justified as a means to raise academic standards and promote equity, its real-world impact tells a different story.
The inequitable burden of homework becomes starkly evident when considering the resources required to complete it, especially in the digital age. Homework today often necessitates a computer and internet access – resources not readily available to all students. This digital divide significantly disadvantages students from lower-income backgrounds, deepening the chasm between them and their more affluent peers.
Key points highlighting the disparities:
- Digital Inequity: Many students lack access to necessary technology for homework, with low-income families disproportionately affected.
- Impact of COVID-19: The pandemic exacerbated these disparities as education shifted online, revealing the extent of the digital divide.
- Educational Outcomes Tied to Income: A critical indicator of college success is linked more to family income levels than to rigorous academic preparation. Research indicates that while 77% of students from high-income families graduate from highly competitive colleges, only 9% from low-income families achieve the same . This disparity suggests that the pressure of heavy homework loads, rather than leveling the playing field, may actually hinder the chances of success for less affluent students.
Moreover, the approach to homework varies significantly across different types of schools. While some rigorous private and preparatory schools in both marginalized and affluent communities assign extreme levels of homework, many progressive schools focusing on holistic learning and self-actualization opt for no homework, yet achieve similar levels of college and career success. This contrast raises questions about the efficacy and necessity of heavy homework loads in achieving educational outcomes.
The issue of homework and its inequitable impact is not just an academic concern; it is a reflection of broader societal inequalities. By continuing practices that disproportionately burden students from less privileged backgrounds, the educational system inadvertently perpetuates the very disparities it seeks to overcome.
3. Negative Impact on Family Dynamics

Homework, a staple of the educational system, is often perceived as a necessary tool for academic reinforcement. However, its impact extends beyond the realm of academics, significantly affecting family dynamics. The negative repercussions of homework on the home environment have become increasingly evident, revealing a troubling pattern that can lead to conflict, mental health issues, and domestic friction.
A study conducted in 2015 involving 1,100 parents sheds light on the strain homework places on family relationships. The findings are telling:
- Increased Likelihood of Conflicts: Families where parents did not have a college degree were 200% more likely to experience fights over homework.
- Misinterpretations and Misunderstandings: Parents often misinterpret their children’s difficulties with homework as a lack of attention in school, leading to feelings of frustration and mistrust on both sides.
- Discriminatory Impact: The research concluded that the current approach to homework disproportionately affects children whose parents have lower educational backgrounds, speak English as a second language, or belong to lower-income groups.
The issue is not confined to specific demographics but is a widespread concern. Samantha Hulsman, a teacher featured in Education Week Teacher , shared her personal experience with the toll that homework can take on family time. She observed that a seemingly simple 30-minute assignment could escalate into a three-hour ordeal, causing stress and strife between parents and children. Hulsman’s insights challenge the traditional mindset about homework, highlighting a shift towards the need for skills such as collaboration and problem-solving over rote memorization of facts.
The need of the hour is to reassess the role and amount of homework assigned to students. It’s imperative to find a balance that facilitates learning and growth without compromising the well-being of the family unit. Such a reassessment would not only aid in reducing domestic conflicts but also contribute to a more supportive and nurturing environment for children’s overall development.
4. Consumption of Free Time

In recent years, a growing chorus of voices has raised concerns about the excessive burden of homework on students, emphasizing how it consumes their free time and impedes their overall well-being. The issue is not just the quantity of homework, but its encroachment on time that could be used for personal growth, relaxation, and family bonding.
Authors Sara Bennett and Nancy Kalish , in their book “The Case Against Homework,” offer an insightful window into the lives of families grappling with the demands of excessive homework. They share stories from numerous interviews conducted in the mid-2000s, highlighting the universal struggle faced by families across different demographics. A poignant account from a parent in Menlo Park, California, describes nightly sessions extending until 11 p.m., filled with stress and frustration, leading to a soured attitude towards school in both the child and the parent. This narrative is not isolated, as about one-third of the families interviewed expressed feeling crushed by the overwhelming workload.
Key points of concern:
- Excessive Time Commitment: Students, on average, spend over 6 hours in school each day, and homework adds significantly to this time, leaving little room for other activities.
- Impact on Extracurricular Activities: Homework infringes upon time for sports, music, art, and other enriching experiences, which are as crucial as academic courses.
- Stifling Creativity and Self-Discovery: The constant pressure of homework limits opportunities for students to explore their interests and learn new skills independently.
The National Education Association (NEA) and the National PTA (NPTA) recommend a “10 minutes of homework per grade level” standard, suggesting a more balanced approach. However, the reality often far exceeds this guideline, particularly for older students. The impact of this overreach is profound, affecting not just academic performance but also students’ attitudes toward school, their self-confidence, social skills, and overall quality of life.
Furthermore, the intense homework routine’s effectiveness is doubtful, as it can overwhelm students and detract from the joy of learning. Effective learning builds on prior knowledge in an engaging way, but excessive homework in a home setting may be irrelevant and uninteresting. The key challenge is balancing homework to enhance learning without overburdening students, allowing time for holistic growth and activities beyond academics. It’s crucial to reassess homework policies to support well-rounded development.
5. Challenges for Students with Learning Disabilities
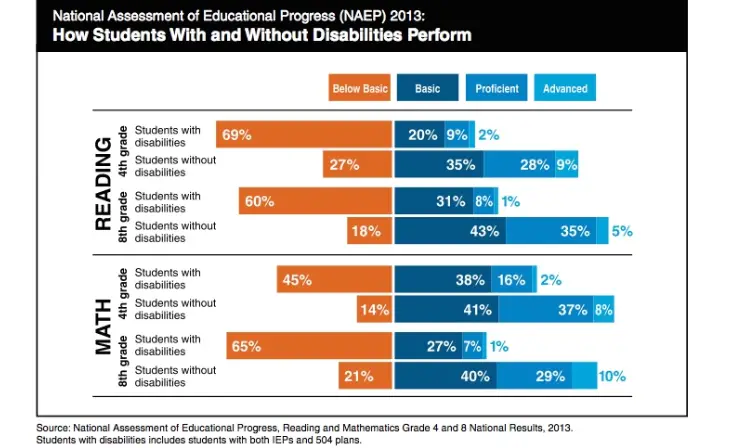
Homework, a standard educational tool, poses unique challenges for students with learning disabilities, often leading to a frustrating and disheartening experience. These challenges go beyond the typical struggles faced by most students and can significantly impede their educational progress and emotional well-being.
Child psychologist Kenneth Barish’s insights in Psychology Today shed light on the complex relationship between homework and students with learning disabilities:
- Homework as a Painful Endeavor: For students with learning disabilities, completing homework can be likened to “running with a sprained ankle.” It’s a task that, while doable, is fraught with difficulty and discomfort.
- Misconceptions about Laziness: Often, children who struggle with homework are perceived as lazy. However, Barish emphasizes that these students are more likely to be frustrated, discouraged, or anxious rather than unmotivated.
- Limited Improvement in School Performance: The battles over homework rarely translate into significant improvement in school for these children, challenging the conventional notion of homework as universally beneficial.
These points highlight the need for a tailored approach to homework for students with learning disabilities. It’s crucial to recognize that the traditional homework model may not be the most effective or appropriate method for facilitating their learning. Instead, alternative strategies that accommodate their unique needs and learning styles should be considered.
In conclusion, the conventional homework paradigm needs reevaluation, particularly concerning students with learning disabilities. By understanding and addressing their unique challenges, educators can create a more inclusive and supportive educational environment. This approach not only aids in their academic growth but also nurtures their confidence and overall development, ensuring that they receive an equitable and empathetic educational experience.
6. Critique of Underlying Assumptions about Learning
The longstanding belief in the educational sphere that more homework automatically translates to more learning is increasingly being challenged. Critics argue that this assumption is not only flawed but also unsupported by solid evidence, questioning the efficacy of homework as an effective learning tool.
Alfie Kohn , a prominent critic of homework, aptly compares students to vending machines in this context, suggesting that the expectation of inserting an assignment and automatically getting out of learning is misguided. Kohn goes further, labeling homework as the “greatest single extinguisher of children’s curiosity.” This critique highlights a fundamental issue: the potential of homework to stifle the natural inquisitiveness and love for learning in children.
The lack of concrete evidence supporting the effectiveness of homework is evident in various studies:
- Marginal Effectiveness of Homework: A study involving 28,051 high school seniors found that the effectiveness of homework was marginal, and in some cases, it was counterproductive, leading to more academic problems than solutions.
- No Correlation with Academic Achievement: Research in “ National Differences, Global Similarities ” showed no correlation between homework and academic achievement in elementary students, and any positive correlation in middle or high school diminished with increasing homework loads.
- Increased Academic Pressure: The Teachers College Record published findings that homework adds to academic pressure and societal stress, exacerbating performance gaps between students from different socioeconomic backgrounds.
These findings bring to light several critical points:
- Quality Over Quantity: According to a recent article in Monitor on Psychology , experts concur that the quality of homework assignments, along with the quality of instruction, student motivation, and inherent ability, is more crucial for academic success than the quantity of homework.
- Counterproductive Nature of Excessive Homework: Excessive homework can lead to more academic challenges, particularly for students already facing pressures from other aspects of their lives.
- Societal Stress and Performance Gaps: Homework can intensify societal stress and widen the academic performance divide.
The emerging consensus from these studies suggests that the traditional approach to homework needs rethinking. Rather than focusing on the quantity of assignments, educators should consider the quality and relevance of homework, ensuring it truly contributes to learning and development. This reassessment is crucial for fostering an educational environment that nurtures curiosity and a love for learning, rather than extinguishing it.
7. Issues with Homework Enforcement, Reliability, and Temptation to Cheat
In the academic realm, the enforcement of homework is a subject of ongoing debate, primarily due to its implications on student integrity and the true value of assignments. The challenges associated with homework enforcement often lead to unintended yet significant issues, such as cheating, copying, and a general undermining of educational values.
Key points highlighting enforcement challenges:
- Difficulty in Enforcing Completion: Ensuring that students complete their homework can be a complex task, and not completing homework does not always correlate with poor grades.
- Reliability of Homework Practice: The reliability of homework as a practice tool is undermined when students, either out of desperation or lack of understanding, choose shortcuts over genuine learning. This approach can lead to the opposite of the intended effect, especially when assignments are not well-aligned with the students’ learning levels or interests.
- Temptation to Cheat: The issue of cheating is particularly troubling. According to a report by The Chronicle of Higher Education , under the pressure of at-home assignments, many students turn to copying others’ work, plagiarizing, or using creative technological “hacks.” This tendency not only questions the integrity of the learning process but also reflects the extreme stress that homework can induce.
- Parental Involvement in Completion: As noted in The American Journal of Family Therapy , this raises concerns about the authenticity of the work submitted. When parents complete assignments for their children, it not only deprives the students of the opportunity to learn but also distorts the purpose of homework as a learning aid.
In conclusion, the challenges of homework enforcement present a complex problem that requires careful consideration. The focus should shift towards creating meaningful, manageable, and quality-driven assignments that encourage genuine learning and integrity, rather than overwhelming students and prompting counterproductive behaviors.
Addressing Opposing Views on Homework Practices
While opinions on homework policies are diverse, understanding different viewpoints is crucial. In the following sections, we will examine common arguments supporting homework assignments, along with counterarguments that offer alternative perspectives on this educational practice.
1. Improvement of Academic Performance

Homework is commonly perceived as a means to enhance academic performance, with the belief that it directly contributes to better grades and test scores. This view posits that through homework, students reinforce what they learn in class, leading to improved understanding and retention, which ultimately translates into higher academic achievement.
However, the question of why students should not have homework becomes pertinent when considering the complex relationship between homework and academic performance. Studies have indicated that excessive homework doesn’t necessarily equate to higher grades or test scores. Instead, too much homework can backfire, leading to stress and fatigue that adversely affect a student’s performance. Reuters highlights an intriguing correlation suggesting that physical activity may be more conducive to academic success than additional homework, underscoring the importance of a holistic approach to education that prioritizes both physical and mental well-being for enhanced academic outcomes.
2. Reinforcement of Learning

Homework is traditionally viewed as a tool to reinforce classroom learning, enabling students to practice and retain material. However, research suggests its effectiveness is ambiguous. In instances where homework is well-aligned with students’ abilities and classroom teachings, it can indeed be beneficial. Particularly for younger students , excessive homework can cause burnout and a loss of interest in learning, counteracting its intended purpose.
Furthermore, when homework surpasses a student’s capability, it may induce frustration and confusion rather than aid in learning. This challenges the notion that more homework invariably leads to better understanding and retention of educational content.
3. Development of Time Management Skills

Homework is often considered a crucial tool in helping students develop important life skills such as time management and organization. The idea is that by regularly completing assignments, students learn to allocate their time efficiently and organize their tasks effectively, skills that are invaluable in both academic and personal life.
However, the impact of homework on developing these skills is not always positive. For younger students, especially, an overwhelming amount of homework can be more of a hindrance than a help. Instead of fostering time management and organizational skills, an excessive workload often leads to stress and anxiety . These negative effects can impede the learning process and make it difficult for students to manage their time and tasks effectively, contradicting the original purpose of homework.
4. Preparation for Future Academic Challenges

Homework is often touted as a preparatory tool for future academic challenges that students will encounter in higher education and their professional lives. The argument is that by tackling homework, students build a foundation of knowledge and skills necessary for success in more advanced studies and in the workforce, fostering a sense of readiness and confidence.
Contrarily, an excessive homework load, especially from a young age, can have the opposite effect . It can instill a negative attitude towards education, dampening students’ enthusiasm and willingness to embrace future academic challenges. Overburdening students with homework risks disengagement and loss of interest, thereby defeating the purpose of preparing them for future challenges. Striking a balance in the amount and complexity of homework is crucial to maintaining student engagement and fostering a positive attitude towards ongoing learning.
5. Parental Involvement in Education

Homework often acts as a vital link connecting parents to their child’s educational journey, offering insights into the school’s curriculum and their child’s learning process. This involvement is key in fostering a supportive home environment and encouraging a collaborative relationship between parents and the school. When parents understand and engage with what their children are learning, it can significantly enhance the educational experience for the child.
However, the line between involvement and over-involvement is thin. When parents excessively intervene by completing their child’s homework, it can have adverse effects . Such actions not only diminish the educational value of homework but also rob children of the opportunity to develop problem-solving skills and independence. This over-involvement, coupled with disparities in parental ability to assist due to variations in time, knowledge, or resources, may lead to unequal educational outcomes, underlining the importance of a balanced approach to parental participation in homework.
Exploring Alternatives to Homework and Finding a Middle Ground

In the ongoing debate about the role of homework in education, it’s essential to consider viable alternatives and strategies to minimize its burden. While completely eliminating homework may not be feasible for all educators, there are several effective methods to reduce its impact and offer more engaging, student-friendly approaches to learning.
Alternatives to Traditional Homework
- Project-Based Learning: This method focuses on hands-on, long-term projects where students explore real-world problems. It encourages creativity, critical thinking, and collaborative skills, offering a more engaging and practical learning experience than traditional homework. For creative ideas on school projects, especially related to the solar system, be sure to explore our dedicated article on solar system projects .
- Flipped Classrooms: Here, students are introduced to new content through videos or reading materials at home and then use class time for interactive activities. This approach allows for more personalized and active learning during school hours.
- Reading for Pleasure: Encouraging students to read books of their choice can foster a love for reading and improve literacy skills without the pressure of traditional homework assignments. This approach is exemplified by Marion County, Florida , where public schools implemented a no-homework policy for elementary students. Instead, they are encouraged to read nightly for 20 minutes . Superintendent Heidi Maier’s decision was influenced by research showing that while homework offers minimal benefit to young students, regular reading significantly boosts their learning. For book recommendations tailored to middle school students, take a look at our specially curated article .
Ideas for Minimizing Homework
- Limiting Homework Quantity: Adhering to guidelines like the “ 10-minute rule ” (10 minutes of homework per grade level per night) can help ensure that homework does not become overwhelming.
- Quality Over Quantity: Focus on assigning meaningful homework that is directly relevant to what is being taught in class, ensuring it adds value to students’ learning.
- Homework Menus: Offering students a choice of assignments can cater to diverse learning styles and interests, making homework more engaging and personalized.
- Integrating Technology: Utilizing educational apps and online platforms can make homework more interactive and enjoyable, while also providing immediate feedback to students. To gain deeper insights into the role of technology in learning environments, explore our articles discussing the benefits of incorporating technology in classrooms and a comprehensive list of educational VR apps . These resources will provide you with valuable information on how technology can enhance the educational experience.
For teachers who are not ready to fully eliminate homework, these strategies offer a compromise, ensuring that homework supports rather than hinders student learning. By focusing on quality, relevance, and student engagement, educators can transform homework from a chore into a meaningful component of education that genuinely contributes to students’ academic growth and personal development. In this way, we can move towards a more balanced and student-centric approach to learning, both in and out of the classroom.
Useful Resources
- Is homework a good idea or not? by BBC
- The Great Homework Debate: What’s Getting Lost in the Hype
- Alternative Homework Ideas
The evidence and arguments presented in the discussion of why students should not have homework call for a significant shift in homework practices. It’s time for educators and policymakers to rethink and reformulate homework strategies, focusing on enhancing the quality, relevance, and balance of assignments. By doing so, we can create a more equitable, effective, and student-friendly educational environment that fosters learning, well-being, and holistic development.
- “Here’s what an education expert says about that viral ‘no-homework’ policy”, Insider
- “John Hattie on BBC Radio 4: Homework in primary school has an effect of zero”, Visible Learning
- HowtoLearn.com
- “Time Spent On Homework Statistics [Fresh Research]”, Gitnux
- “Stress in America”, American Psychological Association (APA)
- “Homework hurts high-achieving students, study says”, The Washington Post
- “National Sleep Foundation’s updated sleep duration recommendations: final report”, National Library of Medicine
- “A multi-method exploratory study of stress, coping, and substance use among high school youth in private schools”, Frontiers
- “The Digital Revolution is Leaving Poorer Kids Behind”, Statista
- “The digital divide has left millions of school kids behind”, CNET
- “The Digital Divide: What It Is, and What’s Being Done to Close It”, Investopedia
- “COVID-19 exposed the digital divide. Here’s how we can close it”, World Economic Forum
- “PBS NewsHour: Biggest Predictor of College Success is Family Income”, America’s Promise Alliance
- “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background”, Taylor & Francis Online
- “What Do You Mean My Kid Doesn’t Have Homework?”, EducationWeek
- “Excerpt From The Case Against Homework”, Penguin Random House Canada
- “How much homework is too much?”, neaToday
- “The Nation’s Report Card: A First Look: 2013 Mathematics and Reading”, National Center for Education Statistics
- “Battles Over Homework: Advice For Parents”, Psychology Today
- “How Homework Is Destroying Teens’ Health”, The Lion’s Roar
- “ Breaking the Homework Habit”, Education World
- “Testing a model of school learning: Direct and indirect effects on academic achievement”, ScienceDirect
- “National Differences, Global Similarities: World Culture and the Future of Schooling”, Stanford University Press
- “When school goes home: Some problems in the organization of homework”, APA PsycNet
- “Is homework a necessary evil?”, APA PsycNet
- “Epidemic of copying homework catalyzed by technology”, Redwood Bark
- “High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame”, The Chronicle of Higher Education
- “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background”, ResearchGate
- “Kids who get moving may also get better grades”, Reuters
- “Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Research, 1987–2003”, SageJournals
- “Is it time to get rid of homework?”, USAToday
- “Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework”, Stanford
- “Florida school district bans homework, replaces it with daily reading”, USAToday
- “Encouraging Students to Read: Tips for High School Teachers”, wgu.edu
- Recent Posts

Simona Johnes is the visionary being the creation of our project. Johnes spent much of her career in the classroom working with students. And, after many years in the classroom, Johnes became a principal.
- Overview of 22 Low-Code Agencies for MVP, Web, or Mobile App Development - October 23, 2024
- Tips to Inspire Your Young Child to Pursue a Career in Nursing - July 24, 2024
- How Parents Can Advocate for Their Children’s Journey into Forensic Nursing - July 24, 2024
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
21 Reasons Why Homework Should Be Banned

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

The homework debate has strong arguments on both sides. Commonly-cited reasons why homework should be banned include the idea that it is often counterproductive, stifles students’ creativity, and limits their freedom outside the classroom.
Students already have up to 7 hours of schoolwork to complete 5 days a week; adding more contributes to increased anxiety, burnout, and overall poor performance.
But arguments for homework include the fact it does increase student grades (Cooper, Robinson & Patall, 2006), it instils discipline, and it helps to reinforce what was learned into long-term memory.
The following are common arguments for banning homework – note that this is an article written to stimulate debate points on the topic, so it only presents one perspective. For the other side of the argument, it’s worth checking out my article on the 27 pros and cons of homework .
Reasons Why Homework Should Be Banned
1. it contributes to increased anxiety.
If there’s one word that describes middle-school and high-school students, it’s anxiety. In my homework statistics article , I cite research showing that 74% of students cite homework as a source of stress.
They have so much to juggle, from the novelty of adolescence to the realization that they must soon start preparing for college and their life after (Pressman et al., 2015).
It’s a lot to manage, and adding homework that reduces their free time and makes them even more restricted is downright harmful. The natural outcome of this dogpile of pressure is anxiety, and many students often feel overwhelmed, both by the hours and hours of coursework in a day and the extensive homework they are assigned (Galloway, Conner & Pope, 2013).
Because teachers often don’t communicate with one another over curricula, major assignments can overlap such that students have to tackle numerous large projects at once, which contributes to severe anxiety over good grades.
In response to this, some students check out of school entirely, letting their academic future go to waste. While, of course, it’s not fair to strawman and say that homework is to blame for all these cases, it may indeed by a contributing factor.
2. It Offers Less Social Time
Homework cuts out free time. Children already spend the better part of their day learning in a school environment, and when they come home, they need to socialize.
Whether it’s family or friends, a social balance is important. Depending on the coursework they’re assigned, homework can detrimentally affect students’ social life, which feed back into more of our first gripe about homework: its anxiety-inducing nature.
Furthermore, social time is extremely important for children to grow up well-balanced and confident. If a child is highly intelligent (book smart) but lacks to social skills we might call street smarts , they may struggle in adulthood.
3. It Detracts from Play Time
Play is extremely important for children’s physical, social, and cognitive development . In fact, children naturally learn through play .
So, when children get home from school, they need a few hours to play. They’re actually learning when playing! If playing with friends, they’re learning social skills; but playing alone also stimulates creative and analytical thinking skills.
Play is also a different type of learning than the learning that commonly happens at school. So, allowing children to play at home gives their brain a break from ‘school learning’ and lets them learn through active and even relaxing methods.
4. It Discourages Physical Exercise and Contributes to Obesity
Exercise is an important part of life for everyone, but especially for children. Developing a positive self-image and disciplining oneself is an important skill to learn, one that becomes much more difficult when homework is in the picture.
Homework can demand a lot of attention that kids could be spending exercising or socializing. These two important life pursuits can be left by the wayside, leaving students feeling confused, depressed, and anxious about the future.
Physical exercise should be considered a key feature of a child’s holistic development. It helps keep children healthy, can reduce anxiety, and support healthy immune systems. It also helps with physical development such as supporting fine and gross motor skills .
In fact, some scholars (Ren et al., 2017) have even identified excessive homework as a contributing factor for childhood obesity.
5. It Disrupts Sleep Patterns
Everyone knows the trope of a college student staying up late to finish their homework or cram for a test.
While it would be unfair to credit homework exclusively for an unhealthy sleep schedule, the constant pressure to finish assignments on time often yields one of two results.
Students can either burn the midnight oil to make sure their homework is done, or they can check out of school entirely and ignore their academic interests. Neither is an acceptable way to live.
This point is particularly pertinent to teenagers. They are not lazy; teens need 12-13 hours of sleep every day because their bodies are changing so dramatically.
To pile additional homework on them that interferes with the circadian rhythm is not just unhelpful—it may be downright harmful (Yeo et al., 2020).
6. It Involves Less Guidance
If there’s one thing that’s beneficial about the in-person learning experience, it’s the ability to raise one’s hand and let the teacher know when something is unclear or difficult to understand.
That handheld process isn’t available for homework; in fact, homework matters little in the grand scheme of learning. It’s just busywork that’s supposed to help students consolidate their knowledge.
In reality, homework becomes something that students resent and can fill them with feelings of frustration—something that would be much more readily addressed if the same content was covered in-person with a teacher to guide the student through the assignment.
7. It’s Regularly Rote Learning
In most subjects, homework isn’t reflective of the skills students need to learn to thrive in the workforce. Instead, it often simply involves rote learning (repetition of tasks) that is not seen as the best way to learn.
A main goal of education is to train up vocational professionals with defined skills. But more often than not, homework winds up as a bland set of word problems that have no basis in the real world.
Walking through real-world examples under the guidance of a teacher is much more beneficial to student learning.
8. It Can Detract from a Love of Learning
If you know what it’s like to doze off during a boring class or meeting, then you can relate to the difficulty students have paying attention in class.
That motivation starts to dwindle when students must complete assignments on their own time, often under immense pressure.
It’s not a healthy way to inspire kids to learn about different subjects and develop a love of learning.
Students already need to sit through hours and hours of class on end in-person. This learning time should be used more effectively to eliminate the need for home.
When children finally get out of class at the end of the day, they need to socialize and exercise, not spend even longer staring at a book to complete a bunch of unhelpful practice questions.
9. It Convolutes the Subject
Another important consideration about homework is that it can often be counterproductive.
That’s because teachers don’t always use the full curriculum material for their teaching, and they may choose to develop their own homework rather than to use the resources offered by the curriculum provider.
This homework can often be off-subject, extremely niche, or unhelpful in explaining a subject that students are studying.
Students who don’t understand a subject and don’t have resources to rely on will eventually give up. That risk becomes even more prevalent when you factor in the scope, complexity, and type of assignment.
Students need to be taught in a safe environment where they can feel free to ask questions and learn at their own pace. Of course, there’s no fairytale way to perfect this ideal, but what is clear is that homework is not beneficial to the learning environment for many students.
10. It’s Not What Kids Want
Lastly, homework should be banned because it’s generally not what students want. From elementary to college level, most students harbor some sort of resentment towards homework.
It might be easy to dismiss this to say that the students “aren’t living in the real world.” The truth of the matter is that the real world is a lot more nuanced, creative, and diverse than the repetitive, broad, and often stagnant homework.
It’s easy to understand why most students wish that more time in school had been spent on learning how to live rather than trying to figure out how many apples Johnny had. Subjects like car maintenance, entrepreneurship, computer skills, socialization, networking, tax filing, finances, and survival are touched on at best and ignored at worst.
It’s not enough for students to be able to regurgitate information on a piece of paper; in the end, the education system should teach them how to be self-sufficient, something that might be much easier to do if resources were divested from homework and poured into more beneficial subject material.
Consider these 11 Additional Reasons
- Decreases time with parents – Homework may prevent parents and children from spending quality time together.
- Hidden costs – Families often feel pressure to purchase internet and other resources to help their children to complete their homework.
- Is inequitable – some children have parents to help them while others don’t. Similarly, some children have internet access to help while others don’t (see: Kralovec & Buell, 2001).
- Easy to cheat – Unsupervised homework time makes it easy for children to simply cheat on their work so they can get on with play time!
- Lack of downtime – Children need time where they aren’t doing anything. Time that is unstructured helps them to develop hobbies and interests .
- Detracts from reading – Children could be spending their time reading books and developing their imaginations rather than working on repetitive homework tasks.
- Take up parental time – Parents, who have just spent all day working, are increasingly expected to spend their time doing ‘teaching’ with their children at home.
- Discourages club membership – If children are too busy with homework, they may not be able to join clubs and sporting groups that can help them make friends and develop extracurricular skills.
- Makes it hard for college students to make a living – In college, where homework is extensive, students often can’t juggle homework with their weekend and night-time jobs. As a result, it pushes them further into student poverty.
- Contributes to poor work-life culture – From early ages, we’re sending a message to children that they should take their work home with them. This can spill over into the workplace, where they’ll be expected to continue working for their company even after the workday ends.
- Can reinforce faulty learning – When children learn in isolation during homework time, they may end up practicing their work completely wrong! They need intermittent support to make sure their practice is taking them down the right path.
Students may need to demonstrate their understanding of a topic to progress; that, at least, is a reflection of the real world. What’s not helpful is when students are peppered day and night with information that they need to regurgitate on a piece of paper.
For positive outcomes to come from homework, parents and teachers need to work together. It depends a lot on the type of homework provided as well as the age of the student and the need to balance homework with time to do other things in your life.
Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003. Review of educational research , 76 (1), 1-62.
Galloway, M., Conner, J., & Pope, D. (2013). Nonacademic effects of homework in privileged, high-performing high schools. The journal of experimental education , 81 (4), 490-510. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00220973.2012.745469
Kralovec, E., & Buell, J. (2001). The end of homework: How homework disrupts families, overburdens children, and limits learning . Beacon Press.
Pressman, R. M., Sugarman, D. B., Nemon, M. L., Desjarlais, J., Owens, J. A., & Schettini-Evans, A. (2015). Homework and family stress: With consideration of parents’ self confidence, educational level, and cultural background. The American Journal of Family Therapy , 43 (4), 297-313. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/01926187.2015.1061407
Ren, H., Zhou, Z., Liu, W., Wang, X., & Yin, Z. (2017). Excessive homework, inadequate sleep, physical inactivity and screen viewing time are major contributors to high paediatric obesity. Acta Paediatrica , 106 (1), 120-127. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.13640
Yeo, S. C., Tan, J., Lo, J. C., Chee, M. W., & Gooley, J. J. (2020). Associations of time spent on homework or studying with nocturnal sleep behavior and depression symptoms in adolescents from Singapore. Sleep Health , 6 (6), 758-766. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2020.04.011

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
5 thoughts on “21 Reasons Why Homework Should Be Banned”
very helpful website thanks
my topic on publics speaking is on banning homework it really helps
Very helpful cheers mate
This really helped my debate team
It is very helpful for me.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

10 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework
Exploring the benefits of a no-homework policy, this article delves into the traditional perspective that homework is fundamental for reinforcing classroom lessons, instilling discipline, and fostering student responsibility. Yet, a burgeoning amount of research challenges this notion, suggesting that abolishing homework could significantly augment academic outcomes and student well-being. Within the context of innovative student council ideas , we will outline ten persuasive arguments for schools to adopt a no-homework policy, underscoring the comprehensive advantages of this strategy. These benefits include promoting independent learning, equalizing educational opportunities, encouraging creative thinking, and improving physical health. By considering a shift towards no homework, educational institutions can potentially transform the learning experience, making it more effective, enjoyable, and equitable for all students.
For those seeking additional support, services like WritePaper provide a platform for students to receive assistance with their writing tasks, further alleviating the pressures of traditional homework assignments.
Enhanced Family Time
The benefits of no homework start with enriched family interactions. Without the burden of homework, students have more time to spend with family, fostering stronger bonds and allowing for valuable life lessons that aren’t taught in classrooms. This quality time can significantly improve communication within the family, helping parents and children understand each other better. It also allows parents to share their knowledge and experiences, offering a different perspective on life and learning. Furthermore, family time can help relieve the stress and pressure of school, creating a more balanced and nurturing environment for children to grow.
Increased Extracurricular Engagement
A no-homework policy opens up opportunities for students to explore extracurricular activities. Whether it’s sports, arts, or community service, engaging in these activities can lead to a well-rounded education, promoting teamwork, leadership, and time management skills. Such involvement enriches students’ educational experience and helps them discover new passions and talents. Moreover, extracurricular activities provide practical experiences that build character and prepare students for the challenges of the real world. They encourage students to set goals, work towards them, and celebrate their achievements, fostering a sense of accomplishment and self-worth that transcends academic success.
Reduced Stress and Burnout
One of the most significant benefits of having no homework is reducing stress and burnout among students. Excessive homework can lead to sleep deprivation, anxiety, and depression. By removing this stressor, students can maintain better mental health and improve their overall quality of life. This alleviation of stress enhances academic performance and contributes to more positive social interactions and increased participation in class. It allows students to approach their studies with a refreshed mind and a more focused attitude, ultimately leading to a deeper and more meaningful engagement with their education. Furthermore, a healthier state of mind enables students to tackle challenges with resilience and adaptability, essential for success inside and outside the classroom.
Encourages Independent Learning
Contrary to the belief that homework is necessary for reinforcing learning, a no-homework policy can encourage students to pursue knowledge independently, fostering a love for learning that is self-directed and driven by curiosity rather than obligation. This approach empowers students to take charge of their education, seeking information and resources that interest them. It nurtures critical thinking and research skills as students learn to question, analyze, and synthesize information from various sources. Moreover, independent learning encourages students to set academic goals and develop strategies to achieve them, instilling a sense of responsibility and self-motivation. This autonomy in learning prepares students for the demands of higher education and a lifelong journey of personal and professional growth.
Improved Sleep
Numerous studies link excessive homework to sleep deprivation. With no homework benefits, including more rest, students can improve their concentration, memory, and learning ability, leading to better academic performance.
More Time for Personal Development
The benefits of no homework extend to personal development. Students have more time to explore personal interests, develop hobbies, and engage in activities contributing to their identity and self-esteem.
Better Classroom Engagement
Without the fatigue and stress of homework, students are likelier to be engaged and participative in class. This creates a more vibrant learning environment where students feel motivated to contribute.
Equalizes Educational Opportunities
Why students should not have homework: This stance argues for eliminating homework to foster equity and equal educational opportunities. Homework disproportionately impacts students from lower socioeconomic backgrounds, as they may lack access to essential resources or a conducive study environment at home. A no-homework policy can level the playing field, giving all students a fair chance to succeed academically. Such a policy acknowledges the diverse home environments and resource availability, aiming to reduce educational disparities and support inclusive learning for every student.

Encourages Creative Thinking
Why students should not have homework: The benefits of not having homework include encouraging creative thinking. By eliminating homework, students gain more free time, enabling them to delve into creative pursuits and exercise critical thinking beyond structured academic tasks. This newfound freedom can spark innovative ideas and solutions, nurturing invaluable creativity skills essential in academic environments and real-world scenarios. By prioritizing creative exploration, students develop a more well-rounded intellect and problem-solving abilities, preparing them for future challenges.
Healthier Lifestyles
Finally, the benefits of no homework include promoting healthier lifestyles. With extra time, students can engage in physical activities, pursue interests that contribute to their physical well-being, and balance work and leisure, leading to healthier, happier lives.
While homework has traditionally been viewed as an essential component of education, the benefits of no homework present a compelling case for reevaluating its role in how to get good grades in middle school . By fostering family time, reducing stress, encouraging independent learning, and promoting a healthier lifestyle, a no-homework policy can significantly enhance students’ educational experience and well-being. As educators and policymakers reflect on these benefits and how they contribute to achieving good grades in middle school, it’s crucial to consider innovative approaches to learning that prioritize student well-being and holistic development over traditional homework assignments.
Related Posts
Best online jobs for college students.
- March 26, 2024
How to Earn Money as a College Student
- March 20, 2024
How to Be a Good College Student: A Comprehensive Guide
- March 12, 2024
How to Get Good Grades in Middle School
Is Homework Good for Kids? Here’s What the Research Says
A s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day.
The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in Texas went viral last week , earning praise from parents across the country who lament the heavy workload often assigned to young students. Brandy Young told parents she would not formally assign any homework this year, asking students instead to eat dinner with their families, play outside and go to bed early.
But the question of how much work children should be doing outside of school remains controversial, and plenty of parents take issue with no-homework policies, worried their kids are losing a potential academic advantage. Here’s what you need to know:
For decades, the homework standard has been a “10-minute rule,” which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 minutes of homework each night. High school seniors should complete about two hours of homework each night. The National PTA and the National Education Association both support that guideline.
But some schools have begun to give their youngest students a break. A Massachusetts elementary school has announced a no-homework pilot program for the coming school year, lengthening the school day by two hours to provide more in-class instruction. “We really want kids to go home at 4 o’clock, tired. We want their brain to be tired,” Kelly Elementary School Principal Jackie Glasheen said in an interview with a local TV station . “We want them to enjoy their families. We want them to go to soccer practice or football practice, and we want them to go to bed. And that’s it.”
A New York City public elementary school implemented a similar policy last year, eliminating traditional homework assignments in favor of family time. The change was quickly met with outrage from some parents, though it earned support from other education leaders.
New solutions and approaches to homework differ by community, and these local debates are complicated by the fact that even education experts disagree about what’s best for kids.
The research
The most comprehensive research on homework to date comes from a 2006 meta-analysis by Duke University psychology professor Harris Cooper, who found evidence of a positive correlation between homework and student achievement, meaning students who did homework performed better in school. The correlation was stronger for older students—in seventh through 12th grade—than for those in younger grades, for whom there was a weak relationship between homework and performance.
Cooper’s analysis focused on how homework impacts academic achievement—test scores, for example. His report noted that homework is also thought to improve study habits, attitudes toward school, self-discipline, inquisitiveness and independent problem solving skills. On the other hand, some studies he examined showed that homework can cause physical and emotional fatigue, fuel negative attitudes about learning and limit leisure time for children. At the end of his analysis, Cooper recommended further study of such potential effects of homework.
Despite the weak correlation between homework and performance for young children, Cooper argues that a small amount of homework is useful for all students. Second-graders should not be doing two hours of homework each night, he said, but they also shouldn’t be doing no homework.
Not all education experts agree entirely with Cooper’s assessment.
Cathy Vatterott, an education professor at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, supports the “10-minute rule” as a maximum, but she thinks there is not sufficient proof that homework is helpful for students in elementary school.
“Correlation is not causation,” she said. “Does homework cause achievement, or do high achievers do more homework?”
Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs , thinks there should be more emphasis on improving the quality of homework tasks, and she supports efforts to eliminate homework for younger kids.
“I have no concerns about students not starting homework until fourth grade or fifth grade,” she said, noting that while the debate over homework will undoubtedly continue, she has noticed a trend toward limiting, if not eliminating, homework in elementary school.
The issue has been debated for decades. A TIME cover in 1999 read: “Too much homework! How it’s hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.” The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push for better math and science education in the U.S. The ensuing pressure to be competitive on a global scale, plus the increasingly demanding college admissions process, fueled the practice of assigning homework.
“The complaints are cyclical, and we’re in the part of the cycle now where the concern is for too much,” Cooper said. “You can go back to the 1970s, when you’ll find there were concerns that there was too little, when we were concerned about our global competitiveness.”
Cooper acknowledged that some students really are bringing home too much homework, and their parents are right to be concerned.
“A good way to think about homework is the way you think about medications or dietary supplements,” he said. “If you take too little, they’ll have no effect. If you take too much, they can kill you. If you take the right amount, you’ll get better.”
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Where Trump 2.0 Will Differ From 1.0
- How Elon Musk Became a Kingmaker
- The Power—And Limits—of Peer Support
- The 100 Must-Read Books of 2024
- Column: If Optimism Feels Ridiculous Now, Try Hope
- The Future of Climate Action Is Trade Policy
- FX’s Say Nothing Is the Must-Watch Political Thriller of 2024
- Merle Bombardieri Is Helping People Make the Baby Decision
Write to Katie Reilly at [email protected]
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Health & Nursing
Courses and certificates.
- Bachelor's Degrees
- View all Business Bachelor's Degrees
- Business Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Healthcare Administration – B.S.
- Human Resource Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Marketing – B.S.
- Accounting – B.S. Business Administration
- Finance – B.S.
- Supply Chain and Operations Management – B.S.
- Communications – B.S.
- User Experience Design – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree (from the School of Technology)
- Health Information Management – B.S. (from the Leavitt School of Health)
- View all Business Degrees
Master's Degrees
- View all Business Master's Degrees
- Master of Business Administration (MBA)
- MBA Information Technology Management
- MBA Healthcare Management
- Management and Leadership – M.S.
- Accounting – M.S.
- Marketing – M.S.
- Human Resource Management – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration (from the Leavitt School of Health)
- Data Analytics – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Information Technology Management – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed. (from the School of Education)
Certificates
- Supply Chain
- Accounting Fundamentals
- Digital Marketing and E-Commerce
Bachelor's Preparing For Licensure
- View all Education Bachelor's Degrees
- Elementary Education – B.A.
- Special Education and Elementary Education (Dual Licensure) – B.A.
- Special Education (Mild-to-Moderate) – B.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary)– B.S.
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– B.S.
- View all Education Degrees
Bachelor of Arts in Education Degrees
- Educational Studies – B.A.
Master of Science in Education Degrees
- View all Education Master's Degrees
- Curriculum and Instruction – M.S.
- Educational Leadership – M.S.
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed.
Master's Preparing for Licensure
- Teaching, Elementary Education – M.A.
- Teaching, English Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Science Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Special Education (K-12) – M.A.
Licensure Information
- State Teaching Licensure Information
Master's Degrees for Teachers
- Mathematics Education (K-6) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grade) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- English Language Learning (PreK-12) – M.A.
- Endorsement Preparation Program, English Language Learning (PreK-12)
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– M.A.
- View all Technology Bachelor's Degrees
- Cloud Computing – B.S.
- Computer Science – B.S.
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – B.S.
- Data Analytics – B.S.
- Information Technology – B.S.
- Network Engineering and Security – B.S.
- Software Engineering – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration (from the School of Business)
- User Experience Design – B.S. (from the School of Business)
- View all Technology Master's Degrees
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – M.S.
- Data Analytics – M.S.
- Information Technology Management – M.S.
- MBA Information Technology Management (from the School of Business)
- Full Stack Engineering
- Web Application Deployment and Support
- Front End Web Development
- Back End Web Development
- ServiceNow Application Developer
3rd Party Certifications
- IT Certifications Included in WGU Degrees
- View all Technology Degrees
- View all Health & Nursing Bachelor's Degrees
- Nursing (RN-to-BSN online) – B.S.
- Nursing (Prelicensure) – B.S. (Available in select states)
- Health Information Management – B.S.
- Health and Human Services – B.S.
- Psychology – B.S.
- Health Science – B.S.
- Public Health – B.S.
- Healthcare Administration – B.S. (from the School of Business)
- View all Nursing Post-Master's Certificates
- Nursing Education—Post-Master's Certificate
- Nursing Leadership and Management—Post-Master's Certificate
- Family Nurse Practitioner—Post-Master's Certificate
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner —Post-Master's Certificate
- View all Health & Nursing Degrees
- View all Nursing & Health Master's Degrees
- Nursing – Education (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Family Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Education (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration
- Master of Public Health
- MBA Healthcare Management (from the School of Business)
- Business Leadership (with the School of Business)
- Supply Chain (with the School of Business)
- Accounting Fundamentals (with the School of Business)
- Digital Marketing and E-Commerce (with the School of Business)
- Back End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Front End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Web Application Deployment and Support (with the School of Technology)
- Full Stack Engineering (with the School of Technology)
- ServiceNow Application Developer (with the School of Technology)
- Single Courses
Apply for Admission
Admission requirements.
- New Students
- WGU Returning Graduates
- WGU Readmission
- Enrollment Checklist
- Accessibility
- Accommodation Request
- School of Education Admission Requirements
- School of Business Admission Requirements
- School of Technology Admission Requirements
- Leavitt School of Health Admission Requirements
Additional Requirements
- Computer Requirements
- No Standardized Testing
- Clinical and Student Teaching Information
Transferring
- FAQs about Transferring
- Transfer to WGU
- Transferrable Certifications
- Request WGU Transcripts
- International Transfer Credit
- Tuition and Fees
- Financial Aid
- Scholarships
Other Ways to Pay for School
- Tuition—School of Business
- Tuition—School of Education
- Tuition—School of Technology
- Tuition—Leavitt School of Health
- Your Financial Obligations
- Tuition Comparison
- Applying for Financial Aid
- State Grants
- Consumer Information Guide
- Responsible Borrowing Initiative
- Higher Education Relief Fund
FAFSA Support
- Net Price Calculator
- FAFSA Simplification
- See All Scholarships
- Military Scholarships
- State Scholarships
- Scholarship FAQs
Payment Options
- Payment Plans
- Corporate Reimbursement
- Current Student Hardship Assistance
- Military Tuition Assistance
WGU Experience
- How You'll Learn
- Scheduling/Assessments
- Accreditation
- Student Support/Faculty
- Military Students
- Part-Time Options
- Virtual Military Education Resource Center
- Student Outcomes
- Return on Investment
- Students and Gradutes
- Career Growth
- Student Resources
- Communities
- Testimonials
- Career Guides
- Skills Guides
- Online Degrees
- All Degrees
- Explore Your Options
Admissions & Transfers
- Admissions Overview
Tuition & Financial Aid
Student Success
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Military and Veterans
- Commencement
- Careers at WGU
- Advancement & Giving
- Partnering with WGU
Should Students Have Homework?
- Classroom Strategies
- See More Tags

By Suzanne Capek Tingley, Veteran Educator, M.A. Degree
It used to be that students were the only ones complaining about the practice of assigning homework. For years, teachers and parents thought that homework was a necessary tool when educating children. But studies about the effectiveness of homework have been conflicting and inconclusive, leading some adults to argue that homework should become a thing of the past.
What Research Says about Homework
According to Duke professor Harris Cooper, it's important that students have homework. His meta-analysis of homework studies showed a correlation between completing homework and academic success, at least in older grades. He recommends following a "10 minute rule" : students should receive 10 minutes of homework per day in first grade, and 10 additional minutes each subsequent year, so that by twelfth grade they are completing 120 minutes of homework daily.
But his analysis didn't prove that students did better because they did homework; it simply showed a correlation . This could simply mean that kids who do homework are more committed to doing well in school. Cooper also found that some research showed that homework caused physical and emotional stress, and created negative attitudes about learning. He suggested that more research needed to be done on homework's effect on kids.
Some researchers say that the question isn't whether kids should have homework. It's more about what kind of homework students have and how much. To be effective, homework has to meet students' needs. For example, some middle school teachers have found success with online math homework that's adapted to each student's level of understanding. But when middle school students were assigned more than an hour and a half of homework, their math and science test scores went down .
Researchers at Indiana University discovered that math and science homework may improve standardized test grades, but they found no difference in course grades between students who did homework and those who didn't. These researchers theorize that homework doesn't result in more content mastery, but in greater familiarity with the kinds of questions that appear on standardized tests. According to Professor Adam Maltese, one of the study's authors, "Our results hint that maybe homework is not being used as well as it could be."
So while many teachers and parents support daily homework, it's hard to find strong evidence that the long-held practice produces positive results.
Problems with Homework
In an article in Education Week Teacher , teacher Samantha Hulsman said she's frequently heard parents complain that a 30-minute homework assignment turns into a three-hour battle with their kids. Now, she's facing the same problem with her own kids, which has her rethinking her former beliefs about homework. "I think parents expect their children to have homework nightly, and teachers assign daily homework because it's what we've always done," she explained. Today, Hulsman said, it's more important to know how to collaborate and solve problems than it is to know specific facts.
Child psychologist Kenneth Barish wrote in Psychology Today that battles over homework rarely result in a child's improvement in school . Children who don't do their homework are not lazy, he said, but they may be frustrated, discouraged, or anxious. And for kids with learning disabilities, homework is like "running with a sprained ankle. It's doable, but painful."
Barish suggests that parents and kids have a "homework plan" that limits the time spent on homework. The plan should include turning off all devices—not just the student's, but those belonging to all family members.
One of the best-known critics of homework, Alfie Kohn , says that some people wrongly believe "kids are like vending machines—put in an assignment, get out learning." Kohn points to the lack of evidence that homework is an effective learning tool; in fact, he calls it "the greatest single extinguisher of children's curiosity that we have yet invented."
Homework Bans
Last year, the public schools in Marion County, Florida, decided on a no-homework policy for all of their elementary students . Instead, kids read nightly for 20 minutes. Superintendent Heidi Maier said the decision was based on Cooper's research showing that elementary students gain little from homework, but a lot from reading.
Orchard Elementary School in South Burlington, Vermont, followed the same path, substituting reading for homework. The homework policy has four parts : read nightly, go outside and play, have dinner with your family, and get a good night's sleep. Principal Mark Trifilio says that his staff and parents support the idea.
But while many elementary schools are considering no-homework policies, middle schools and high schools have been reluctant to abandon homework. Schools say parents support homework and teachers know it can be helpful when it is specific and follows certain guidelines. For example, practicing solving word problems can be helpful, but there's no reason to assign 50 problems when 10 will do. Recognizing that not all kids have the time, space, and home support to do homework is important, so it shouldn't be counted as part of a student's grade.
So Should Students Have Homework?
Should you ban homework in your classroom? If you teach lower grades, it's possible. If you teach middle or high school, probably not. But all teachers should think carefully about their homework policies. By limiting the amount of homework and improving the quality of assignments, you can improve learning outcomes for your students.
Ready to Start Your Journey?
HEALTH & NURSING
Recommended Articles
Take a look at other articles from WGU. Our articles feature information on a wide variety of subjects, written with the help of subject matter experts and researchers who are well-versed in their industries. This allows us to provide articles with interesting, relevant, and accurate information.
{{item.date}}
{{item.preTitleTag}}
{{item.title}}
The university, for students.
- Student Portal
- Alumni Services
Most Visited Links
- Business Programs
- Student Experience
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Student Communities
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Thanksgiving Worksheet Bundle for Last-Minute Activities 🦃
Should Homework Be Banned? Here’s What Real Educators Think
Plus, what research on the subject really tells us.

Every kid dreams of it: “Homework banned forevermore!” For as long as anyone can remember, homework has just been one of those things kids have to do because it’s good for them, like eating their vegetables. But is it really as important to do hours of homework every night as it is to eat broccoli and carrots? New research suggests homework might not have a whole lot of value. This leads to a big question: Should we ban homework?
“I think parents already have enough stress just in providing for their families!” says one Arizona 1st grade teacher. “I can imagine one more chore of having to sit down and do homework with their child would add that much more stress. Kids don’t like doing homework, so it frustrates them, which in turn frustrates parents. They spend time fighting about homework that they could be spending quality time over a board game or family meal!”
We wanted to know more, as every educator should. So, we combed through recent research to see what experts say, and explored the news to see what schools in the United States and abroad have tried. Plus, we asked 40+ active K-12 educators to share their thoughts. Here’s what we found out.
Does homework actually work?
This is one of the biggest questions people have around homework bans. Is it worth the time students are spending on it? How many kids actually do it consistently? How involved do parents need to be? In short: Does homework have value?
What the Research Says
Educators first started asking serious questions about homework more than 20 years ago, when an article that evaluated decades of research on homework suggested that it might not be as effective as we thought, at least in the lower grades . But other studies on homework indicate that students who do homework as assigned have higher academic outcomes overall, especially in grades 7 through 12.
What Real Educators Say
Most of the teachers that responded to our survey felt homework (especially for upper grades) does have at least some value. Many, though, were less concerned with academic benefits and more with developing general life skills like time management and responsibility.
- “For older students, reasonable homework that is preparation for class the next day helps students learn how to manage their time, meet deadlines, and take responsibility for their learning. I am a fan of flipped learning—students watch the lesson for homework and then use class time to ask questions, work together, work with their teacher, and do the work.” —Julie Mason, MS/HS English teacher

- “In middle school and high school, homework is important because it helps build stamina and potential study habits for college or trade schools.” —Desiree T., elementary teacher
- “Homework is good practice for subjects like math. In other subjects, it is good for reviewing subject matter.” —Ohio 8th grade social studies teacher
- “The proper amount of homework that is relevant to the daily lessons will help reinforce the skill and allow parents to see what their child is learning.” —Joanie B., Texas 4th/6th grade teacher
- “It’s not beneficial; parents today have not been taught how to help with new strategies. They are also often so busy that they cannot be bothered to help so they just give the answers. I saw a lot of this during the pandemic and even after when I would have 1st graders tell me they knew the answer ‘because they just know it.’ Not to mention the students who would actually benefit from having the extra practice of homework oftentimes do not have the support at home.” —Georgia 3rd grade teacher
- “In my 8 years of teaching, homework has never been successful for families or me. For the majority of parents and kids, it’s overwhelming. It is also additional work for teachers to manage. This is another extension and overreach of the expectations of the teacher.” —Lauren Anderson, Ohio 4th grade teacher

- “Homework isn’t busy work. How will today’s youth become tomorrow’s leaders (or survive college/trades classes) if they aren’t practicing skills to the next level?” —Arizona 1st grade teacher
Should we ban homework in elementary school?
Most adults today didn’t have homework in kindergarten, so they’re surprised when their child arrives home with a backpack full of worksheets. Older elementary students frequently bring home big projects like making a diorama or creating a family tree, something that usually means a lot of parent involvement. Is homework at this age reasonable and meaningful?
Supporters of a homework ban often cite research from John Hattie, who concluded that elementary school homework has no effect on academic progress. In a podcast he said, “Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero … It’s one of those lower hanging fruits that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, ‘Is it really making a difference?’”
The general wisdom these days seems to point to less homework overall at the elementary level, with one huge exception: reading. The research agrees: kids need to read at home as well as at school. Most educators recommend kids spend at least 20 minutes reading at home every single day.
More than half of our survey respondents (56%) are in favor of banning homework for the elementary grades. They worried about kids not having support or resources at home and taking away their time for creative play or family activities. But some teachers still find value in elementary homework, especially for math and reading, as long as it’s minimal. ADVERTISEMENT

- “The common push for homework in elementary schools is ‘to prepare them for high school.’ That’s overreach. The elementary child’s job is to be an elementary child. We need to teach children where they are.” —Lauren Anderson
- “In elementary school, there should be a mixture of homework and unhomework activities. For example, a homework menu with a list of activities to complete for the month or for the week: Read in pajamas for 20 minutes, complete 3 math sheets, help cook dinner, have a family movie night, write your first and last name 10 times, help pack your snack, etc.” —Desiree T.
- “No homework should be part of the teacher motto—work smarter, not harder. Teachers spend too much time grading homework. I believe teachers and students should commit to making every minute count in the classroom so everyone can go home and just be with family.” —Jennifer N., 5th grade teacher
- “Students are learning new concepts. There is not a guarantee that someone will be able to help them with these tasks. Practicing incorrectly is worse than no practice at all.” —High school resource specialist

- “Kids should be encouraged to read [at home] and spend time with families and friends.” —Elementary English language development teacher
How much homework is enough (or too much)?
If we agree that that answer to “should we ban homework altogether” is “no,” then how much homework is reasonable? The answer seems to vary by grade level, as you would expect. But many point out the need to focus on the quality of homework over the quantity. And there have been increasing calls to let kids enjoy their longer school breaks without homework hanging over their heads .
A 2019 study showed that teenagers have doubled the amount of time they spend on homework since the 1990s. This study found that teens spend about an hour a day doing homework on average, which many would argue isn’t unreasonable. But in another study , kids self-reported doing an average of three hours of homework a night, which seems a lot more significant.
The National PTA and the NEA recommend kids do about 10 minutes of homework per night per grade level. In other words, a 3rd grader should do 30 minutes of homework. A 12th grader would do 120 minutes, or two full hours.

Perhaps more important than “How much homework?” is “What kind of homework?” Meaningful practice of what kids learned in class that day can be helpful. Busywork is not. And assigning really difficult work for kids to tackle at home, without any help from a teacher or other expert voice, is likely to simply frustrate them. Unfortunately, most teachers don’t receive training on how to assign homework that is meaningful and relevant to students. This is another area where we really need to consider a major culture shift.
While 75% of those surveyed say homework has some value in the upper grades at least, most feel it shouldn’t be excessive. Teachers stressed that it should never be used as punishment. Plus, it’s important to remember not all kids have the same access to help and resources outside the classroom.

- “Homework is important but I also believe it shouldn’t exceed 30-60 minutes a night.” —Desiree T.
- “I do think elementary students should practice their reading and maybe 10 minutes of math [at home]. That may look different for each child due to how long it may take them to complete something.” —Wisconsin elementary special education teacher

- “Elementary students are not too young to have homework once or twice a week. More than that would be too much.” —Tanya T., HS ELA teacher
- “In order to prepare students for high school, I feel 20-30 minutes of homework is okay [in elementary school].” —Florida 5th grade teacher
- “A ton of homework in every subject is ridiculous. But having to read parts of a book or an article and do several math problems should not be burdensome. And the benefit of those two things has been documented.” —Teresa Rennie, Pennsylvania 8th grade teacher

- “I encourage my elementary students to read a little every day to develop a love of reading.” —Meenal Parikh, Ohio 1st grade teacher
- “I think some homework is reasonable. Should it be a hindrance to other other activities or a major inconvenience? No. Some is good, but it doesn’t need to be an every-night thing.” —Patrick Danz, Michigan high school ELA teacher
Are there benefits to less (or no) homework?
Some schools have already banned homework, both in the United States and around the world. In April 2024, Poland enacted a homework ban for students in grades 1 through 3. In grades 4 through 8, homework must be optional and can’t count toward a student’s grade. Finnish schools are famous for assigning less homework at all ages , yet continuing to score highly in international rankings. So what are the benefits of freeing kids from homework?
Prioritizing mental health is at the forefront of the homework ban movement. Leaders say they want to give students time to develop other hobbies, relationships, and balance in their lives. When two Utah elementary schools officially banned homework , they found psychologist referrals for anxiety decreased by more than 50%.
In some cases, less or no homework can even have a positive effect on academic outcomes. One high school math teacher dramatically reduced the number of practice problems he asked his students to tackle at home. He also decreased the impact of homework on grades (from 25% to 1%). Now kids had more time to spend on just a few practice problems, and they weren’t stressed about getting them wrong. The result of changes like these? Higher standardized test scores on average.
Some schools have experimented with extending the school day in exchange for eliminating homework. This ensures that kids have more time to do independent work while also ensuring access to expert assistance. After all, not all parents have the time or ability to help with homework. And Internet access isn’t a given in every household. Keeping schoolwork at school means giving all kids equal access to the resources they need.
Teachers worry that kids who spend too much time doing homework are losing out in other areas. They want younger students to have more time to play. Older kids should be able to decompress after spending hours in the classroom. And everyone deserves more opportunities for family time and extracurriculars.
- “The stress and time surrounding homework is unnecessary. Jobs don’t require you take work home so school shouldn’t either. If a kid needs to work more, school could reach out with extra help, but homework is a waste of time. Home is for family time.” —Stephanie G., Maryland 1st grade teacher
- “Homework creates an equity problem. Not all learners have access to the same environment or supports at home as they do in school. The students who have supportive parents and resources (tutors, etc.) will succeed, while others will be penalized.” —Illinois high school teacher

- “If they work at school, they don’t need to work at home. We’re teaching them that it’s okay for someone to tell them how to spend their off-time. School is their job. I don’t like working for free; why should they think that it’s okay?” —North Carolina 1st grade teacher
- “After-school programs, sports, and unstructured play is MUCH more meaningful and impactful for these generations of students.” —Lauren Anderson
- “There are other ways to teach children responsibility and time management than completing homework that will most likely be ungraded.” —4th grade social studies teacher

One Teacher’s Take on the Value of Homework: More Cons Than Pros
One 4th grade social studies teacher from North Carolina shared their thoughts with us in detail. We felt they were worth sharing with a wider audience. (Note: We’ve edited and condensed their words for space and clarity.)
Homework Hurts Families
“There are multiple factors that work together that make homework detrimental to students and their families. Children need to spend time with their parents building relationships of trust and respect. It is difficult because during the limited time families have together, they are forced by the schools to give that up to deal with homework.
“Many parents are unable to answer homework questions to help their children as methodology has changed and evolved. Homework becomes a stressful battlefield. Children with ADHD, autism, and other challenges have such a difficult time keeping focus at school. When they have to do additional work at home, there are increased meltdowns and battles, putting further strains on families.”
Homework’s Time Cost
“Children also have less time to complete work at home due to how overscheduled families have become. Children as young as 3rd grade arrive home from their games as late as 10:00 at night. That is often their first opportunity to sit down to complete their work. When they come to school the next day, they become irritable, unfocused, frustrated, and unable to quickly grasp new material.
“In older grades, teachers don’t plan together and don’t understand how much is required of the student to complete each night. If a high school student has six classes and each teacher assigns only 30 minutes of homework each night, that adds up to three hours. I hear of many teachers that each give an hour each night. I don’t see how it is possible for a high school student to complete six hours of homework every night.
“The additional stress of homework for the teacher, students, and families is not worth it. Give families time to spend together, and free up teacher time by not having to hunt down missing work and reviewing what they are not grading. Allow children to have a better bedtime and avoid meltdowns at home, which lead to additional stress, anxiety, and depression.”

We’d love to hear your thoughts—should homework be banned? Join the discussion in the We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.

You Might Also Like

Help! A Parent Insists They Have the Right To Do Their Child’s Homework for Them
When I called home, she said she has “the right to help my child with his homework to whatever extent I want.” Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critics argue that homework, particularly in excessive amounts, can lead to negative outcomes such as stress, burnout, and a diminished love for learning. Moreover, it often disproportionately affects students from disadvantaged backgrounds, exacerbating educational inequities.
The homework debate has strong arguments on both sides. Commonly-cited reasons why homework should be banned include the idea that it is often counterproductive, stifles students’ creativity, and limits their freedom outside the classroom.
While homework has traditionally been viewed as an essential component of education, the benefits of no homework present a compelling case for reevaluating its role in how to get good grades in middle school. By fostering family time, reducing stress, encouraging independent learning, and promoting a healthier lifestyle, a no-homework policy ...
Schulte encourages parents and caregivers to resist homework. This might include fighting for no-homework policies at their children’s schools, and pushing back against unrealistic homework...
Despite the weak correlation between homework and performance for young children, Cooper argues that a small amount of homework is useful for all students. Second-graders should not be doing...
Excessive homework can also lead to cheating: 90% of middle school students and 67% of high school students admit to copying someone else’s homework, and 43% of college students engaged in “unauthorized collaboration” on out-of-class assignments.
But while many elementary schools are considering no-homework policies, middle schools and high schools have been reluctant to abandon homework. Schools say parents support homework and teachers know it can be helpful when it is specific and follows certain guidelines.
Supporters of a homework ban often cite research from John Hattie, who concluded that elementary school homework has no effect on academic progress. In a podcast he said, “Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero …
In a review of studies published from 1987 to 2003, Cooper and his colleagues found that homework was linked to better test scores in high school and, to a lesser degree, in middle school. Yet they found only faint evidence that homework provided academic benefit in elementary school (Review of Educational Research, 2006).
Excessive homework can also lead to cheating: 90% of middle-school students and 67% of high-school students admit to copying someone else’s homework, and 43% of college students engaged in “unauthorized collaboration” on out-of-class assignments.