An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Study designs: Part 1 – An overview and classification
Priya ranganathan, rakesh aggarwal.
- Author information
- Copyright and License information
Address for correspondence: Dr. Priya Ranganathan, Department of Anaesthesiology, Tata Memorial Centre, Ernest Borges Road, Parel, Mumbai - 400 012, Maharashtra, India. E-mail: [email protected]
This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
There are several types of research study designs, each with its inherent strengths and flaws. The study design used to answer a particular research question depends on the nature of the question and the availability of resources. In this article, which is the first part of a series on “study designs,” we provide an overview of research study designs and their classification. The subsequent articles will focus on individual designs.
Keywords: Epidemiologic methods, research design, research methodology
INTRODUCTION
Research study design is a framework, or the set of methods and procedures used to collect and analyze data on variables specified in a particular research problem.
Research study designs are of many types, each with its advantages and limitations. The type of study design used to answer a particular research question is determined by the nature of question, the goal of research, and the availability of resources. Since the design of a study can affect the validity of its results, it is important to understand the different types of study designs and their strengths and limitations.
There are some terms that are used frequently while classifying study designs which are described in the following sections.
A variable represents a measurable attribute that varies across study units, for example, individual participants in a study, or at times even when measured in an individual person over time. Some examples of variables include age, sex, weight, height, health status, alive/dead, diseased/healthy, annual income, smoking yes/no, and treated/untreated.
Exposure (or intervention) and outcome variables
A large proportion of research studies assess the relationship between two variables. Here, the question is whether one variable is associated with or responsible for change in the value of the other variable. Exposure (or intervention) refers to the risk factor whose effect is being studied. It is also referred to as the independent or the predictor variable. The outcome (or predicted or dependent) variable develops as a consequence of the exposure (or intervention). Typically, the term “exposure” is used when the “causative” variable is naturally determined (as in observational studies – examples include age, sex, smoking, and educational status), and the term “intervention” is preferred where the researcher assigns some or all participants to receive a particular treatment for the purpose of the study (experimental studies – e.g., administration of a drug). If a drug had been started in some individuals but not in the others, before the study started, this counts as exposure, and not as intervention – since the drug was not started specifically for the study.
Observational versus interventional (or experimental) studies
Observational studies are those where the researcher is documenting a naturally occurring relationship between the exposure and the outcome that he/she is studying. The researcher does not do any active intervention in any individual, and the exposure has already been decided naturally or by some other factor. For example, looking at the incidence of lung cancer in smokers versus nonsmokers, or comparing the antenatal dietary habits of mothers with normal and low-birth babies. In these studies, the investigator did not play any role in determining the smoking or dietary habit in individuals.
For an exposure to determine the outcome, it must precede the latter. Any variable that occurs simultaneously with or following the outcome cannot be causative, and hence is not considered as an “exposure.”
Observational studies can be either descriptive (nonanalytical) or analytical (inferential) – this is discussed later in this article.
Interventional studies are experiments where the researcher actively performs an intervention in some or all members of a group of participants. This intervention could take many forms – for example, administration of a drug or vaccine, performance of a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure, and introduction of an educational tool. For example, a study could randomly assign persons to receive aspirin or placebo for a specific duration and assess the effect on the risk of developing cerebrovascular events.
Descriptive versus analytical studies
Descriptive (or nonanalytical) studies, as the name suggests, merely try to describe the data on one or more characteristics of a group of individuals. These do not try to answer questions or establish relationships between variables. Examples of descriptive studies include case reports, case series, and cross-sectional surveys (please note that cross-sectional surveys may be analytical studies as well – this will be discussed in the next article in this series). Examples of descriptive studies include a survey of dietary habits among pregnant women or a case series of patients with an unusual reaction to a drug.
Analytical studies attempt to test a hypothesis and establish causal relationships between variables. In these studies, the researcher assesses the effect of an exposure (or intervention) on an outcome. As described earlier, analytical studies can be observational (if the exposure is naturally determined) or interventional (if the researcher actively administers the intervention).
Directionality of study designs
Based on the direction of inquiry, study designs may be classified as forward-direction or backward-direction. In forward-direction studies, the researcher starts with determining the exposure to a risk factor and then assesses whether the outcome occurs at a future time point. This design is known as a cohort study. For example, a researcher can follow a group of smokers and a group of nonsmokers to determine the incidence of lung cancer in each. In backward-direction studies, the researcher begins by determining whether the outcome is present (cases vs. noncases [also called controls]) and then traces the presence of prior exposure to a risk factor. These are known as case–control studies. For example, a researcher identifies a group of normal-weight babies and a group of low-birth weight babies and then asks the mothers about their dietary habits during the index pregnancy.
Prospective versus retrospective study designs
The terms “prospective” and “retrospective” refer to the timing of the research in relation to the development of the outcome. In retrospective studies, the outcome of interest has already occurred (or not occurred – e.g., in controls) in each individual by the time s/he is enrolled, and the data are collected either from records or by asking participants to recall exposures. There is no follow-up of participants. By contrast, in prospective studies, the outcome (and sometimes even the exposure or intervention) has not occurred when the study starts and participants are followed up over a period of time to determine the occurrence of outcomes. Typically, most cohort studies are prospective studies (though there may be retrospective cohorts), whereas case–control studies are retrospective studies. An interventional study has to be, by definition, a prospective study since the investigator determines the exposure for each study participant and then follows them to observe outcomes.
The terms “prospective” versus “retrospective” studies can be confusing. Let us think of an investigator who starts a case–control study. To him/her, the process of enrolling cases and controls over a period of several months appears prospective. Hence, the use of these terms is best avoided. Or, at the very least, one must be clear that the terms relate to work flow for each individual study participant, and not to the study as a whole.
Classification of study designs
Figure 1 depicts a simple classification of research study designs. The Centre for Evidence-based Medicine has put forward a useful three-point algorithm which can help determine the design of a research study from its methods section:[ 1 ]
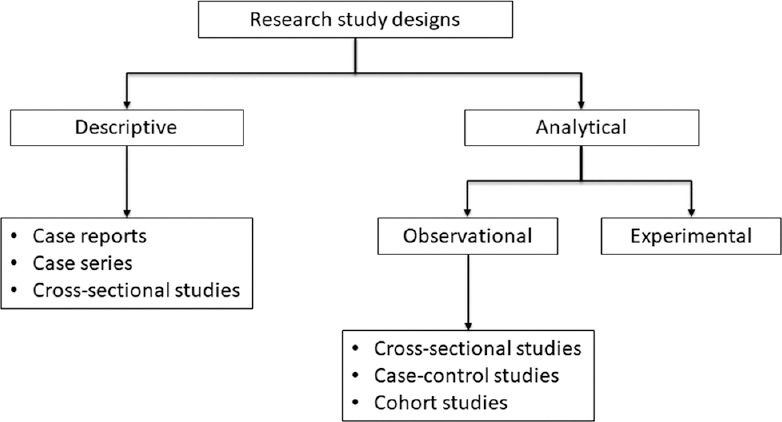
Classification of research study designs
Does the study describe the characteristics of a sample or does it attempt to analyze (or draw inferences about) the relationship between two variables? – If no, then it is a descriptive study, and if yes, it is an analytical (inferential) study
If analytical, did the investigator determine the exposure? – If no, it is an observational study, and if yes, it is an experimental study
If observational, when was the outcome determined? – at the start of the study (case–control study), at the end of a period of follow-up (cohort study), or simultaneously (cross sectional).
In the next few pieces in the series, we will discuss various study designs in greater detail.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
- 1. Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. Study Designs. 2016. [Last accessed on 2018 Sep 04]. Available from: https://www.cebm.net/2014/04/study-designs/
- View on publisher site
- PDF (482.1 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
- En español – ExME
- Em português – EME
An introduction to different types of study design
Posted on 6th April 2021 by Hadi Abbas

Study designs are the set of methods and procedures used to collect and analyze data in a study.
Broadly speaking, there are 2 types of study designs: descriptive studies and analytical studies.
Descriptive studies
- Describes specific characteristics in a population of interest
- The most common forms are case reports and case series
- In a case report, we discuss our experience with the patient’s symptoms, signs, diagnosis, and treatment
- In a case series, several patients with similar experiences are grouped.
Analytical Studies
Analytical studies are of 2 types: observational and experimental.
Observational studies are studies that we conduct without any intervention or experiment. In those studies, we purely observe the outcomes. On the other hand, in experimental studies, we conduct experiments and interventions.
Observational studies
Observational studies include many subtypes. Below, I will discuss the most common designs.
Cross-sectional study:
- This design is transverse where we take a specific sample at a specific time without any follow-up
- It allows us to calculate the frequency of disease ( p revalence ) or the frequency of a risk factor
- This design is easy to conduct
- For example – if we want to know the prevalence of migraine in a population, we can conduct a cross-sectional study whereby we take a sample from the population and calculate the number of patients with migraine headaches.

Cohort study:
- We conduct this study by comparing two samples from the population: one sample with a risk factor while the other lacks this risk factor
- It shows us the risk of developing the disease in individuals with the risk factor compared to those without the risk factor ( RR = relative risk )
- Prospective : we follow the individuals in the future to know who will develop the disease
- Retrospective : we look to the past to know who developed the disease (e.g. using medical records)
- This design is the strongest among the observational studies
- For example – to find out the relative risk of developing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) among smokers, we take a sample including smokers and non-smokers. Then, we calculate the number of individuals with COPD among both.
Case-Control Study:
- We conduct this study by comparing 2 groups: one group with the disease (cases) and another group without the disease (controls)
- This design is always retrospective
- We aim to find out the odds of having a risk factor or an exposure if an individual has a specific disease (Odds ratio)
- Relatively easy to conduct
- For example – we want to study the odds of being a smoker among hypertensive patients compared to normotensive ones. To do so, we choose a group of patients diagnosed with hypertension and another group that serves as the control (normal blood pressure). Then we study their smoking history to find out if there is a correlation.
Experimental Studies
- Also known as interventional studies
- Can involve animals and humans
- Pre-clinical trials involve animals
- Clinical trials are experimental studies involving humans
- In clinical trials, we study the effect of an intervention compared to another intervention or placebo. As an example, I have listed the four phases of a drug trial:
I: We aim to assess the safety of the drug ( is it safe ? )
II: We aim to assess the efficacy of the drug ( does it work ? )
III: We want to know if this drug is better than the old treatment ( is it better ? )
IV: We follow-up to detect long-term side effects ( can it stay in the market ? )
- In randomized controlled trials, one group of participants receives the control, while the other receives the tested drug/intervention. Those studies are the best way to evaluate the efficacy of a treatment.
Finally, the figure below will help you with your understanding of different types of study designs.

References (pdf)
You may also be interested in the following blogs for further reading:
An introduction to randomized controlled trials
Case-control and cohort studies: a brief overview
Cohort studies: prospective and retrospective designs
Prevalence vs Incidence: what is the difference?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
No Comments on An introduction to different types of study design
you are amazing one!! if I get you I’m working with you! I’m student from Ethiopian higher education. health sciences student
Very informative and easy understandable
You are my kind of doctor. Do not lose sight of your objective.
Wow very erll explained and easy to understand
I’m Khamisu Habibu community health officer student from Abubakar Tafawa Balewa university teaching hospital Bauchi, Nigeria, I really appreciate your write up and you have make it clear for the learner. thank you
well understood,thank you so much
Well understood…thanks
Simply explained. Thank You.
Thanks a lot for this nice informative article which help me to understand different study designs that I felt difficult before
That’s lovely to hear, Mona, thank you for letting the author know how useful this was. If there are any other particular topics you think would be useful to you, and are not already on the website, please do let us know.
it is very informative and useful.
thank you statistician
Fabulous to hear, thank you John.
Thanks for this information
Thanks so much for this information….I have clearly known the types of study design Thanks
That’s so good to hear, Mirembe, thank you for letting the author know.
Very helpful article!! U have simplified everything for easy understanding
I’m a health science major currently taking statistics for health care workers…this is a challenging class…thanks for the simified feedback.
That’s good to hear this has helped you. Hopefully you will find some of the other blogs useful too. If you see any topics that are missing from the website, please do let us know!
Hello. I liked your presentation, the fact that you ranked them clearly is very helpful to understand for people like me who is a novelist researcher. However, I was expecting to read much more about the Experimental studies. So please direct me if you already have or will one day. Thank you
Dear Ay. My sincere apologies for not responding to your comment sooner. You may find it useful to filter the blogs by the topic of ‘Study design and research methods’ – here is a link to that filter: https://s4be.cochrane.org/blog/topic/study-design/ This will cover more detail about experimental studies. Or have a look on our library page for further resources there – you’ll find that on the ‘Resources’ drop down from the home page.
However, if there are specific things you feel you would like to learn about experimental studies, that are missing from the website, it would be great if you could let me know too. Thank you, and best of luck. Emma
Great job Mr Hadi. I advise you to prepare and study for the Australian Medical Board Exams as soon as you finish your undergrad study in Lebanon. Good luck and hope we can meet sometime in the future. Regards ;)
You have give a good explaination of what am looking for. However, references am not sure of where to get them from.
Subscribe to our newsletter
You will receive our monthly newsletter and free access to Trip Premium.
Related Articles

Cluster Randomized Trials: Concepts
This blog summarizes the concepts of cluster randomization, and the logistical and statistical considerations while designing a cluster randomized controlled trial.

Expertise-based Randomized Controlled Trials
This blog summarizes the concepts of Expertise-based randomized controlled trials with a focus on the advantages and challenges associated with this type of study.

A well-designed cohort study can provide powerful results. This blog introduces prospective and retrospective cohort studies, discussing the advantages, disadvantages and use of these type of study designs.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Epidemiology of study design.
Swapna Munnangi ; Sameh W. Boktor .
Affiliations
Last Update: April 24, 2023 .
- Introduction
In epidemiology, researchers are interested in measuring or assessing the relationship of exposure with a disease or an outcome. As a first step, they define the hypothesis based on the research question and then decide which study design will be best suited to answer that question. How the researcher conducts the investigation is directed by the chosen study design. The study designs can be broadly classified as experimental or observational based on the approach used to assess whether exposure and an outcome are associated. In an experimental study design, researchers assign patients to intervention and control/comparison groups in an attempt to isolate the effects of the intervention. Being able to control various aspects of the experimental study design enables the researchers to identify causal links between interventions and outcomes of interest. In several instances, an experimental study design may not be feasible or suitable; observational studies are conducted in such situations. As the name indicates, observational studies involve merely observing the patients in a non-controlled environment without actually interfering or manipulating with other aspects of the study and therefore are non-experimental. The observation can be prospective, retrospective, or current, depending on the subtype of an observational study. [1]
Observational Studies
Case-Control Studies
Case-control studies are used to determine the degree of associations between various risk factors and outcomes. The factors that affect the risk of a disease are called exposures. Case-control studies can help identify beneficial or harmful exposures. As the name suggests, there are two groups of patient cases and controls in a case-control study. Cases are patients who have a particular disease, condition, or disability. Controls are those patients that do not have the disease. Typically, researchers identify appropriate representative controls for the cases that they are studying from the general population. Then they retrospectively look in the past for the possible exposures these patients might have had to a risk factor. Selecting the patients for the control group is a very critical component of research based on case-control studies. Due to the retrospective nature of the study design, case-control studies are subject to recall bias. Case-control studies are inexpensive, efficient, and often less time-consuming to conduct. This study design is especially suitable for rare diseases that have long latency periods. [2]
Case-Crossover Studies
Case-crossover studies are helpful to study triggers within an individual. When the researcher is studying a transient exposure or risk factor, the case-crossover design is useful. This is a relatively new study design where there is a case and a control component, both of which come from the same individual. Each case is self-matched by serving as its own control. Determining the control and case components period is a critical and difficult aspect of a case-crossover study. [3]
Cohort Studies
Cohort studies initially classify patients into two groups based on their exposure status. Cohorts are followed over time to see who develops the disease in the exposed and non-exposed groups. Cohort studies can be retrospective or prospective. Incidence can be directly calculated from a cohort study as you begin with exposed and unexposed patients, unlike a case-control study where you start with diseased and non-diseased patients. Relative risk is the measure of effect for a cohort study. Cohort studies are subject to very low recall bias, and multiple outcomes can be studied simultaneously. One of the disadvantages of cohort studies is that they are more prone to selection bias. Studying rare diseases and outcomes that have long follow-up periods can be very expensive and time-consuming using cohort studies. [4]
Cross-Sectional Studies
Cross-sectional studies are observational in nature and give a snapshot of the characteristics of study subjects in a single point of time. Unlike cohort studies, cross-sectional studies do not have a follow-up period and therefore are relatively simple to conduct. As the exposure status/outcome of interest information is collected in a single moment in time, often by surveys, cross-sectional study design cannot provide a cause-effect relationship and is the weakest of the observational designs. This study design is generally used to assess the prevalence of a disease in a population. [5]
Ecological Studies
Ecological studies are used when data at an individual level is unavailable, or large-scale comparisons are needed to study the population-level effect of exposures on a disease condition. Therefore, ecological study results are applicable only at the population level. The types of measures in ecological studies are aggregates of individual-level data. These studies, therefore, are subject to a type of confounding called an ecological fallacy, which occurs when relationships identified at group level data are assumed to be true for individuals. Ecological studies are generally used in public health research. [6]
Experimental Studies
Randomized Clinical Trials
Randomized clinical trials or randomized control trials (RCT) are considered the gold standard of study design. In an RCT, the researcher randomly assigns the subjects to a control group and an experimental group. Randomization in RCT avoids confounding and minimizes selection bias. This enables the researcher to have similar experimental and control groups, thereby enabling them to isolate the effect of an intervention. The experimental group gets the exposure/treatment, which can be an agent involved in causation, prevention, or treatment of a disease. The control group receives no treatment, a placebo treatment, or another standard of care treatment depending on the study's objective. The groups are then followed prospectively to see who develops the outcome of interest. RCT’s are expensive, and researchers using this study design often face issues with the integrity of randomization due to refusals, drops outs, crossovers, and non-compliance. [7] [8]
The key function of an epidemiology study design is to enable the researcher to address the research question with minimal ambiguity logically.
- Issues of Concern
Study design should be well thought of before initiating a research investigation. Choosing an inappropriate study design may undermine overall study validity. Critical thinking about the possible study design issues beforehand will ensure that the research question is adequately addressed.
- Clinical Significance
Study design plays a major role in determining the scientific value of a research study. Understanding the basic study design concepts will aid the clinicians in practicing evidence-based medicine. [9]
- Other Issues
Errors in study design are extremely difficult to correct after study completion. Thorough planning is required to avoid weak conclusions or unconvincing results.
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
All interprofessional healthcare team members, including clinicians, mid-level practitioners, nurses, pharmacists, and therapists, need to be well-versed in the various study designs utilized to perform medical research. Such knowledge can help delineate strong studies and results from weaker ones, determine the clinical applicability of study results, and enhance patient care through the appropriate application of data-driven research results. Failure to understand study design and the strength of data provided by various types of studies can lead to improper decision-making and negatively impact patient outcomes. [10] [Level 5]
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Swapna Munnangi declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Sameh Boktor declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Munnangi S, Boktor SW. Epidemiology Of Study Design. [Updated 2023 Apr 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. [Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022] Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1; 2(2022). Epub 2022 Feb 1.
- Overview of the epidemiology methods and applications: strengths and limitations of observational study designs. [Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2010] Overview of the epidemiology methods and applications: strengths and limitations of observational study designs. Colditz GA. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2010; 50 Suppl 1(s1):10-2.
- Case Control Studies. [StatPearls. 2024] Case Control Studies. Tenny S, Kerndt CC, Hoffman MR. StatPearls. 2024 Jan
- Review Observational designs in clinical multiple sclerosis research: Particulars, practices and potentialities. [Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019] Review Observational designs in clinical multiple sclerosis research: Particulars, practices and potentialities. Jongen PJ. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019 Oct; 35:142-149. Epub 2019 Jul 20.
- Review Healthcare outcomes assessed with observational study designs compared with those assessed in randomized trials. [Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014] Review Healthcare outcomes assessed with observational study designs compared with those assessed in randomized trials. Anglemyer A, Horvath HT, Bero L. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 29; 2014(4):MR000034. Epub 2014 Apr 29.
Recent Activity
- Epidemiology Of Study Design - StatPearls Epidemiology Of Study Design - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In clinical research, our aim is to design a study which would be able to derive a valid and meaningful scientific conclusion using appropriate statistical methods. The conclusions derived from a research study can either improve health care or result in inadvertent harm to patients.
Study design (also referred to as research design) refers to the different study types used in research and evaluation. In the context of an impact/outcome evaluation, study design is the approach used to systematically investigate the effects of an intervention or a program. Study designs may be experimental, quasi-experimental or non ...
Research study design is a framework, or the set of methods and procedures used to collect and analyze data on variables specified in a particular research problem. Research study designs are of many types, each with its advantages and limitations.
Study designs are the set of methods and procedures used to collect and analyze data in a study. Broadly speaking, there are 2 types of study designs: descriptive studies and analytical studies. Descriptive studies
Rich source of ideas, hypotheses about disease, conditions, risk, prognosis and treatment. including a control group (a benefit, strength). Suggested Practice: which support clinical decisions regarding a specific patient scenario. Identify study design by abstract, methods.
In epidemiology, researchers are interested in measuring or assessing the relationship of exposure with a disease or an outcome. As a first step, they define the hypothesis based on the research question and then decide which study design will be best suited to answer that question.